Building websites in Drupal often requires reusing smaller pieces of content within larger ones. For example, a testimonial within a case study, a banner inside a landing page, or a short section within a long-term article. These pieces need to stay connected but also version-safe.
That is exactly what Entity Reference Revisions (ERR) help with. It allows you to link one entity to another while keeping track of specific revisions, ensuring that older published content stays consistent even after edits.
What are Entity Reference Revisions?
Entity Reference Revisions is a field type that extends the regular Entity Reference functionality to include revision tracking. Instead of always linking to the latest version of a referenced entity, it connects to a specific saved revision, preserving content history and stability.
This means that when you update the parent content, Drupal also updates its reference to the appropriate version of the embedded content. Older revisions of the parent content still point to their earlier versions of the embedded items.
As the name suggests, entity reference revisions allow you to edit a section or a block inside a larger entity and ensure that the original version of that parent content remains connected to the current version.
It’s an essential functionality for Drupal modules like Paragraphs and Inline Entity Form. These two include entities (a paragraph or a section) that are parts of bigger entities (a page or an article).
Why are Entity Reference Revisions important?
Without Entity Reference Revisions, you will only find the latest version of the referenced entity on your Drupal site. This can cause serious problems if you rely on version control or editorial approval.
For example, imagine a landing page that includes multiple embedded sections. If someone edits one of those sections later, the update automatically affects the published landing page. That means your live, approved content changes silently, and that’s never good practice.
Entity Reference Revisions prevents that by “locking” each reference to the exact version that existed when the parent content was saved. It preserves the historical link between parent and child entities, making revision comparisons and rollbacks fully reliable.
When should you use Entity Reference Revisions?
You should use Entity Reference Revisions in situations where:
- You have nested content structures (like Paragraphs or Layout Builder sections).
- Each piece of content must maintain its own revision history.
- Editors need to safely update parts of a page without changing the published version.
- Your site uses workflow and moderation, and you want to prevent accidental content drift.
If your content should always show the latest version, for example, a “Contact Information” block or “Global Footer”, then a regular Entity Reference field is enough.
Step-by-step example: Testing Entity Reference Revisions in action
Let’s go through a simple example to understand how ERR works behind the scenes.
Step 1: Enabling Paragraphs (and ERR Automatically)
When you enable the Paragraphs module, the Entity Reference Revisions (ERR) module is automatically enabled as a dependency because Paragraphs use ERR for revision tracking.
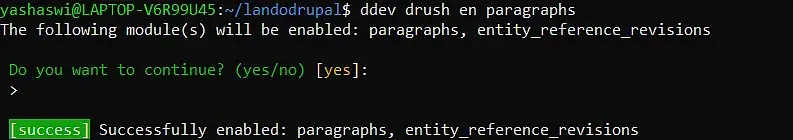
Enabling Paragraphs automatically enables the Entity Reference Revisions module.
Step 2: Creating the First Content (Version 1)
Create a new content type. Add a Paragraph field to it. Here, the Paragraph type includes a body field. Add your first paragraph with some text, and save it as Version 1.
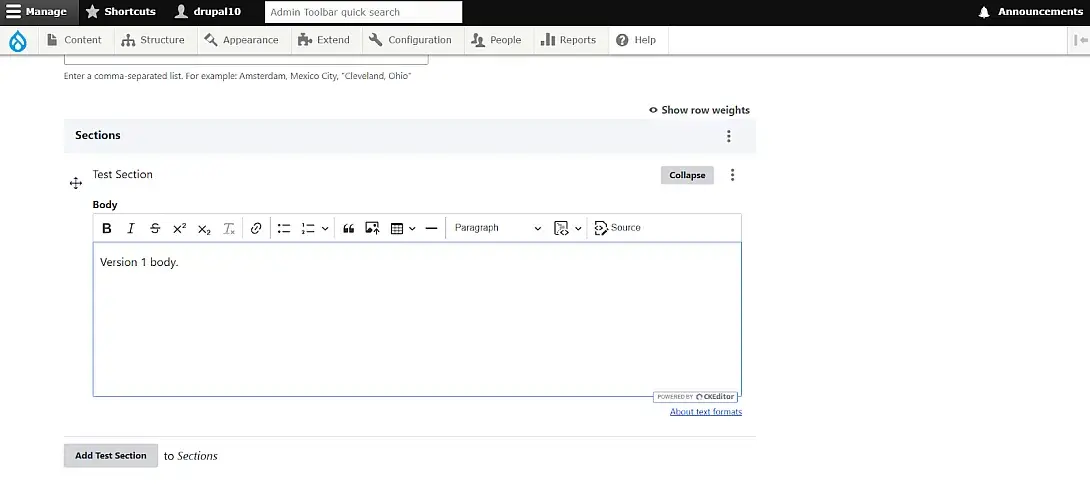
Adding the first version of paragraph content.
Step 3: Editing and Updating Paragraph Content (Version 2)
Edit the same content and change the paragraph text. Save again. This creates a new revision of both the parent entity and the paragraph itself, tracked through ERR.
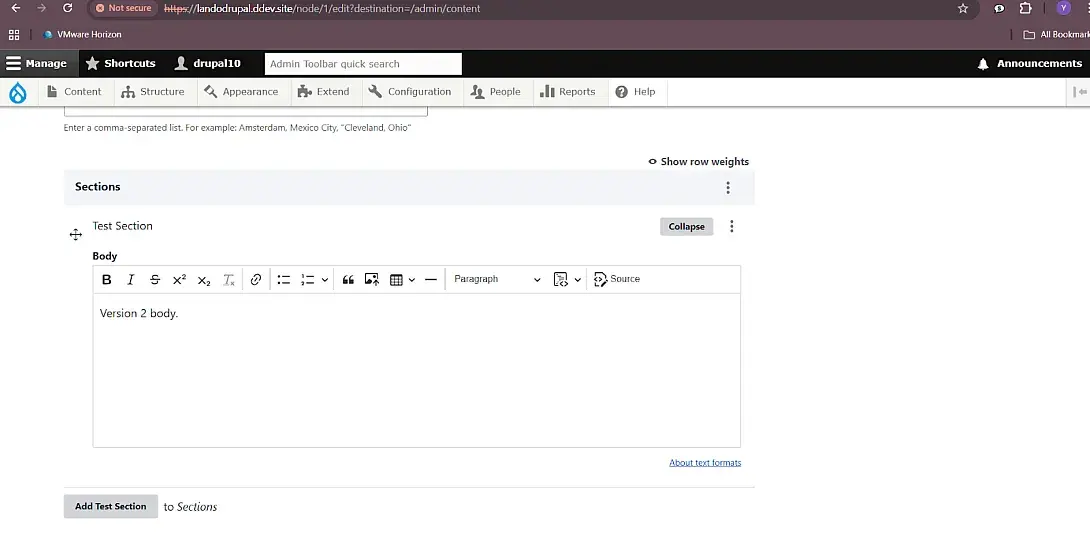
Editing the paragraph creates a new revision tracked by ERR.
Step 4: Checking the Revisions Tab
Open the Revisions tab of your content. You’ll now see two versions - one for the first save and another for the updated one.
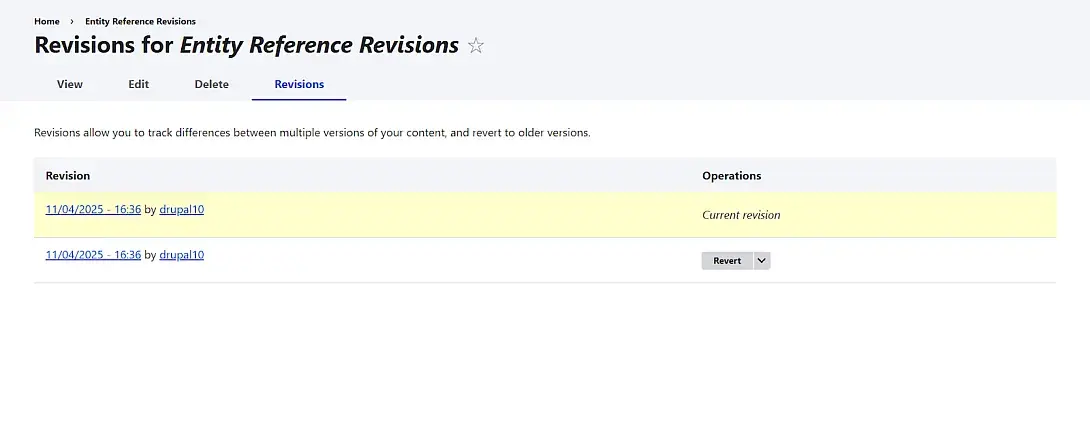
Two content revisions were created after updating paragraph text.
Step 5: Viewing the Difference Between Revisions
View each revision. The older version will show the original paragraph text, while the latest version shows the updated content. This proves that Entity Reference Revisions links each parent revision to the exact paragraph revision that existed at that time.

Older Revision
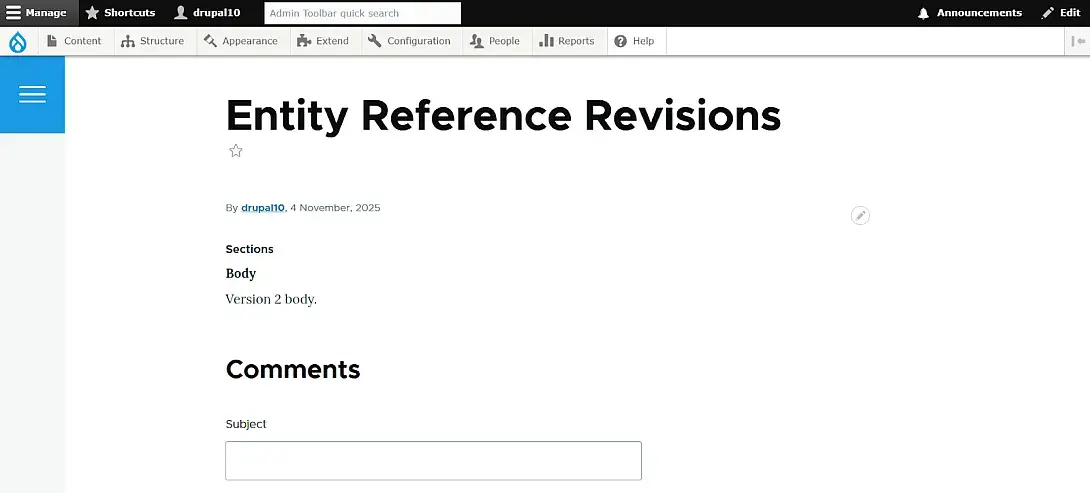
Current revision. Each revision displays its own paragraph version, preserved by Entity Reference Revisions.
Benefits of using Entity Reference Revisions
- Consistent version control: Each piece of content keeps a record of its specific version relationships.
- Accurate revision history: Older revisions always display the correct referenced versions.
- Safe editing experience: Editors can modify sections without worrying about breaking published content.
- Smooth workflow integration: Works perfectly with Paragraphs, Layout Builder, and moderation systems.
- Reliable rollback support: You can safely roll back to earlier revisions, knowing all embedded entities will match their correct versions.
How to enable it
Entity Reference Revisions is part of Drupal core, so you don’t need to download it separately.
To enable it:
- Go to the Extend page in your Drupal admin.
- Search for Entity Reference Revisions.
- Check the box and click Install.
After installing it, you’ll find its purpose while using Paragraphs and Inline Entity Form that rely on it by default.
Final thoughts
Although Entity Reference Revisions might seem like a minor feature, it actually plays a crucial role in Drupal’s content architecture. It’s your safety guard that keeps your older published versions untouched when you edit any part of your current page.
This is what makes complex features like Paragraphs, Layout Builder, and content moderation workflows reliable and safe to use. If you prioritize content integrity and revision control, Entity Reference Revisions are necessary for you!